CarbonCel
your carbon farming assistant

Carbon Farming
Carbon Farming is a whole farm approach to optimizing carbon capture on working landscapes by implementing practices that are known to improve the rate at which CO2 is removed from the atmosphere and stored in plant material and/or soil organic matter. There are many ways to do this: from small adjustments on farm level – like applying fertilizers rich in carbon, reduced or no-tillage, or planting cover crops – to changes in the entire farming system – like enriched crop rotation or agroforestry.
Benefits
Carbon farming practices are guidelines to sequester carbon and/or reduce GHG emissions. Many of these practices are identified as conservation practices that improve soil health and sequester carbon while producing important co-benefits, including: increased soil water holding capacity, biodiversity, and resilience.
Agri-food suppliers companies can work together with farmers and advertise their use of carbon farming on product packaging.
Companies outside the agri-food chain are buying carbon farming certificates to compensate for their own emissions. The financial compensation for the farmer creates an incentive to apply carbon sequestration techniques on the soil, and the local carbon offset creates benefits for these companies, as branding or a positive image or sustainability goals, ending to compensate their emissions.
Carbon projects
Carbon credits, also known as carbon offsets, are permits that allow the owner to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases.
- Carbon credits were devised as a mechanism to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon credits create a monetary incentive for companies to reduce their carbon emissions.
- Companies are buying a number of credits, and over time can sell any excess to other companies.
- Private companies, Farmers, Landlords, through their projects can offer carbon offsets to companies or individuals seeking to reduce their net carbon footprint.
What is CarbonCel
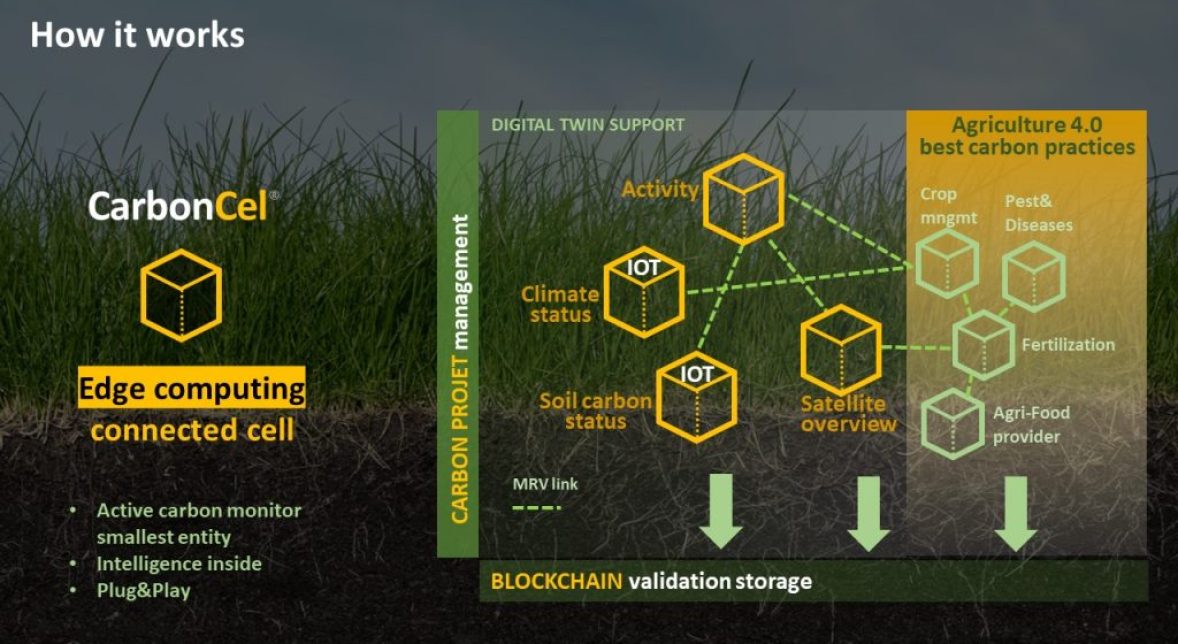
CarbonCel is an end2end advanced solution for carbon farming, supporting carbon project implementation and monitoring. Our solution relies on Agriculture 4.0 use cases, implementing devices, robots and machines telematics, best farming practices reinforced by (AI) algorithms on real-time monitoring data. Solution concept is around connected “cells”… that forms project carbon cells topology.
As you learned, organic cells are the basic “building blocks” of all living things. A living organism is composed of interconnected cells. They provide structure for the organism, assimilate external nutrients , convert them into energy, and carry out specialized functions to store DNA data through interconnectivity. Yes… it is collective organization, where is cell is important.
Similar to this description, a CarbonCel is the smallest living block into a carbon project, having the role to digest the data and provide a carbon info throughput. In reality, carbon cell is an edge computing block that can be interconnected with other blocks, providing data and receiving data.
A carbon cell could be:
- an edge computing device in the middle of the crop that acquiring & processing sensors data
- a specialized edge computing software block that process data from other carbon cells,
- a satellite dat entity, providing hyperspectral crop scanning,
- an agri-food resource provider (that provides chemical fertilizers or pesticides, services etc) for that crop/land
All carbon cells are trained to be interconnected and store the data into Blockchain .

Building your Cel
CarbonCel is also a open for new technologies and usecases. Our framework exposes API to build your own intelligence on specific carbon farming .
Once you build and deploy your CarbonCel entity, this has to be validated based on concrete results and data throughput.
CarbonCel validated entities, you can connect it into various carbon projects chains, adding value on the best practices and/or carbon monitoring.
You can get revenue from your CarbonCels entities based on how much the entities are used and/or how much carbon saves.
Secured data chain
Agri-food supply chains and crop data involve a large number of stakeholders— from small-scale farmers, traders to product manufacturers, activities, sensors & satellite and climate regional data. This complexity limits farm-to-carbon traceability, which is key to identify sustainability-related issues in carbon projects including environmental and soil degradation.
CarbonCel project and monitoring “Cel” data is stored in BlockChain by various stakeholders, “stamping” the carbon project monitoring data as authentical.
The farmer/landlord is the owner of the data that is shared with all carbon project stakeholders.